Electrical Insulator
Electrical Insulators are a vital component used in electrical systems to prevent unwanted flow of current to the earth from their supporting points. Insulators are made of Insulating materials, porcelain, glass, silicone rubber, and so on. They are so insulated that no current can pass through them.
Powerline Insulators are very important for the overhead line, they are used to support the conductor of the transmission line and provide instructions of the tower body, they are connected to electrical conductors without allowing current through themselves.
There are 3 types of insulators according to the insulator material, Ceramic insulator: made of porcelain, Glass insulator: made of glass, and Composite insulator: made of silicone rubber.
Rax Industry insulators include Pin Insulator, Suspension Insulator, Strain Insulator, Spool insulator, Stay Insulator, and so on.
Power line insulators: 7 tips you should know before choosing
Chapter 1:What is an electrical insulator?
Insulators are used to separate line conductors from each other and the supporting structures electrically. Permittivity and dielectric strength of the insulating material are very high so that it can withstand high electrical stress.
Overhead power lines are always supported on insulators mounted on their support poles and towers.
Insulators should have the following properties:
- high mechanical strength to withstand the conductor load, wind load, etc.
- high electrical resistance in order to minimize the leakage currents
- high relative permittivity of insulating material so that the dielectric strength is high
- high ratio of puncture strength to flashover
Chapter 2:Insulator material
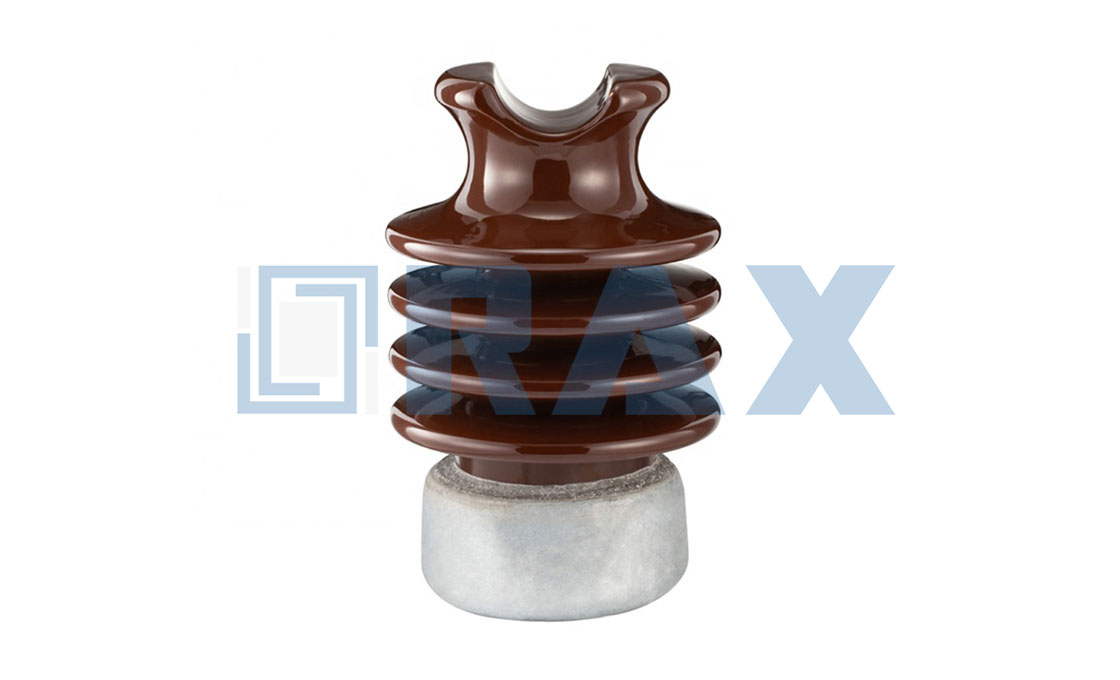
(a) Porcelain insulator
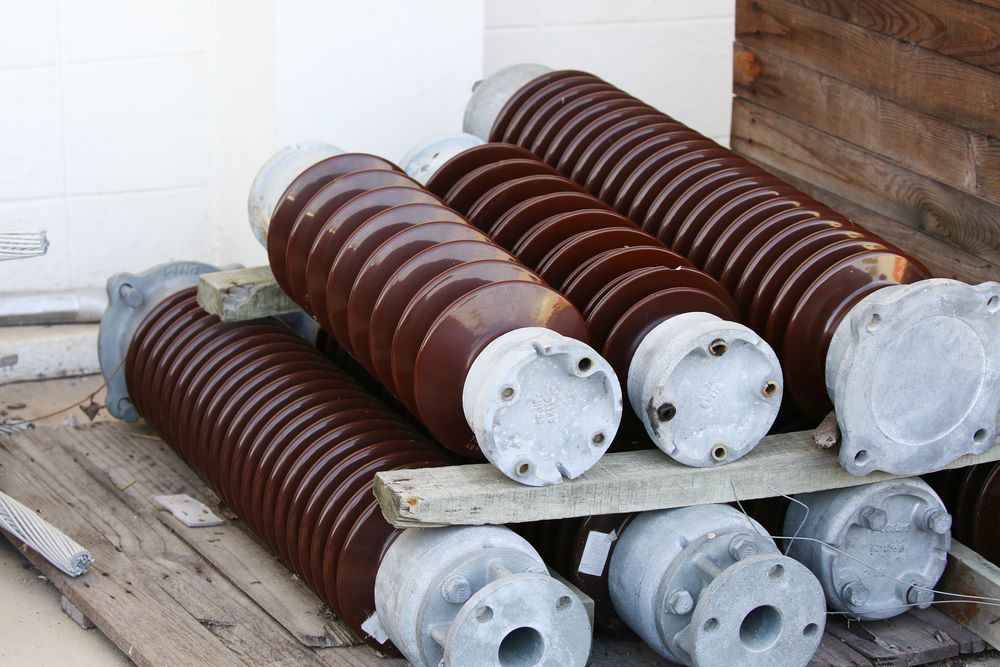

Porcelain Insulator
The most commonly used materials for the overhead line is porcelain. Porcelain is a ceramic material. It is produced by firing at a high temperature a mixture of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz.
The metal parts within the insulator are made of malleable cast iron with galvanizing. It is mechanically stronger than glass, gives less trouble from leakage, and is less affected by temperature change.
Advantage of Porcelain insulator
Environmental friendly. At its disposal, the porcelain insulator is not dangerous waste
Giving a longer useful life in terms of loads generated by electric charges
In the dry state as electric insulation material has better electrical properties than the polymer
Higher resistance to degradation of the surface
Resistant to rodents, termites, birds and other animals capable of compromising the integrity
Suitable for extremely hot/cold changes in the environment
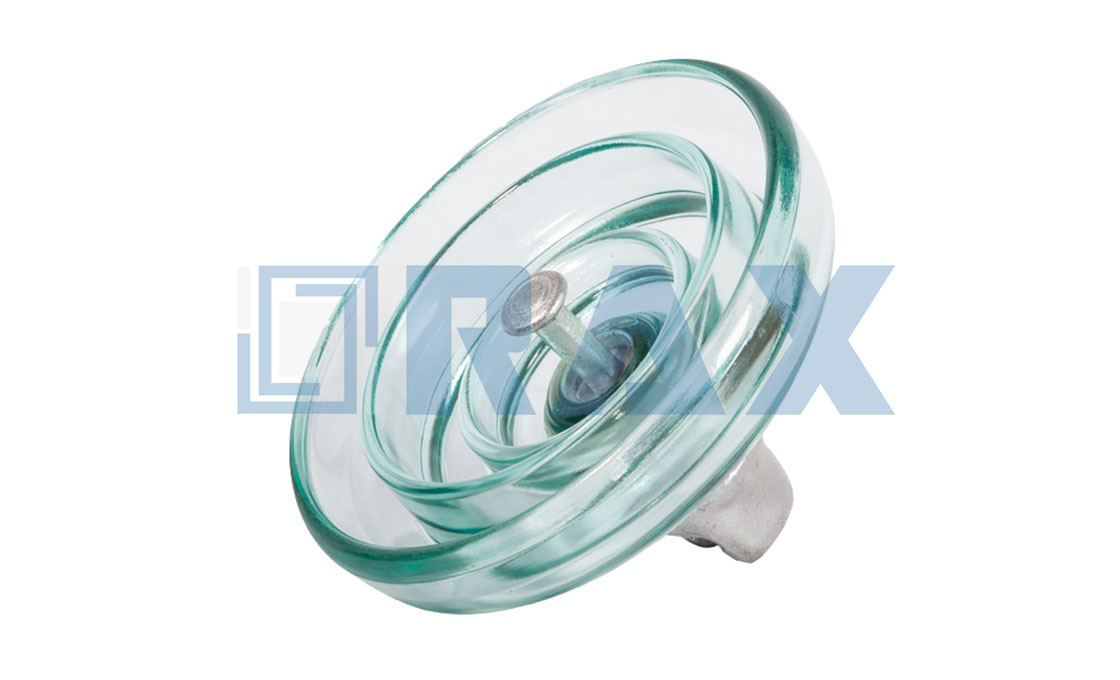
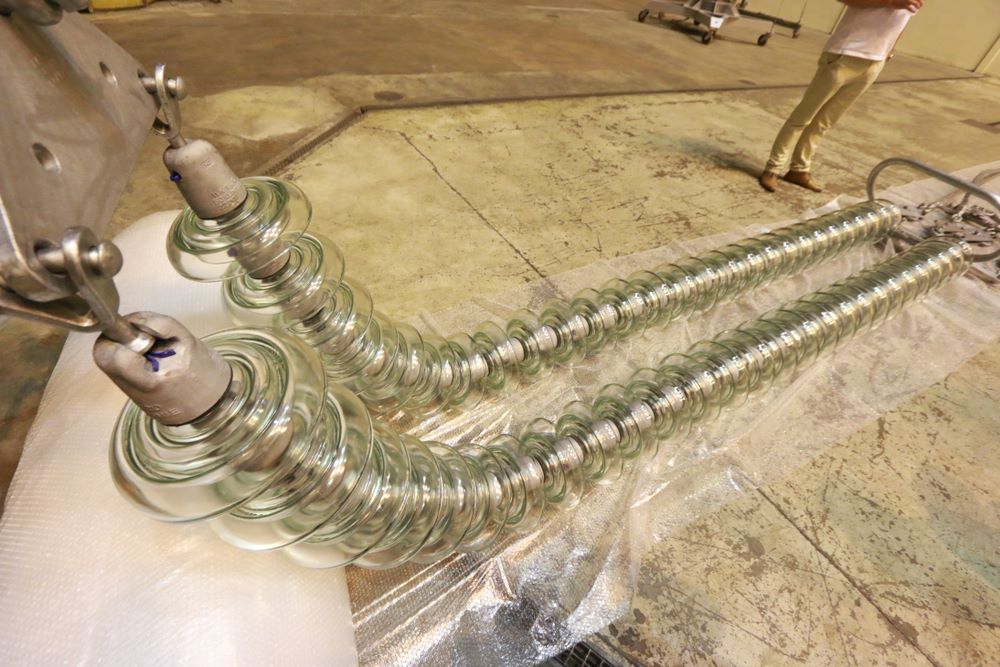
(b) glass insulator
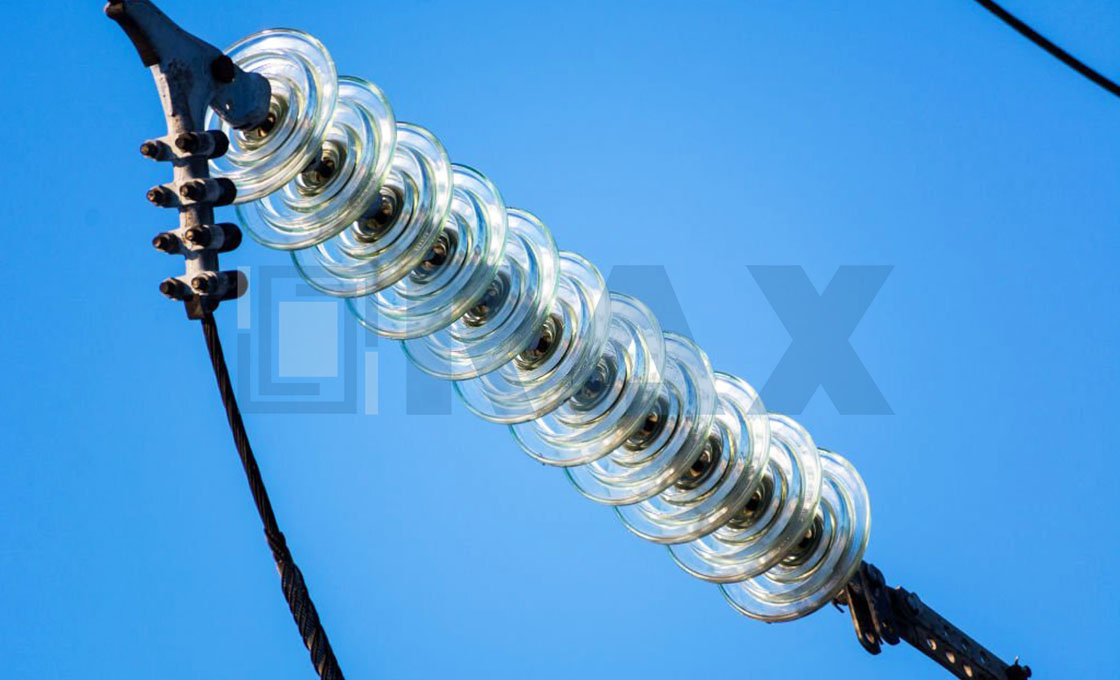

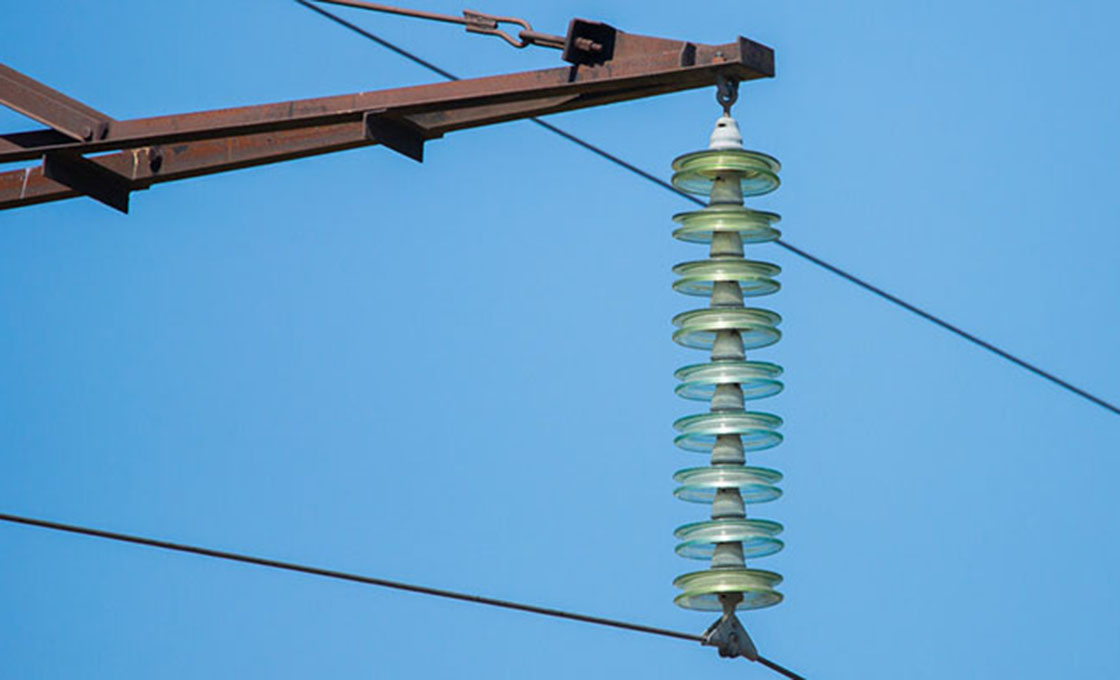
Glass Insulator String
Many times glass is used as insulating material. The glass is made tough by annealing.
Glass insulator has the following advantage:-
High dielectric strength about 140KV per c.m of the thickness of the material.
High resistivity.
Low coefficient of thermal expansion.
High compressive strength than porcelain insulators.
As it is transparent, so any flow impurities air bubbles cracks, impurities, etc. can be easily detected.
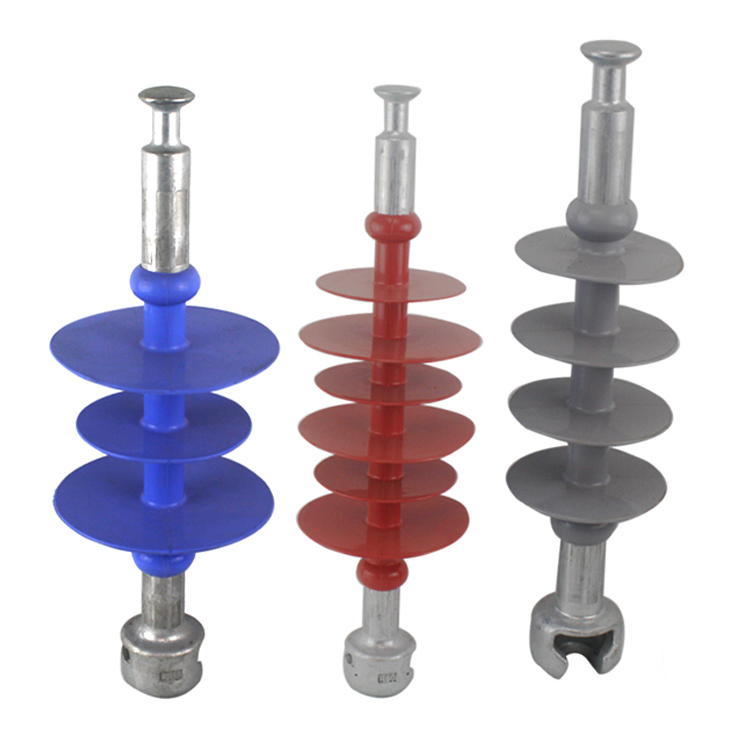
(c) Composite insulator
Composite Insulator
Composite polymer insulators have two insulating parts such as fiberglass core and a metal equipped with metal end fittings.
Advantage of polymer insulator
Small volume and lightweight, easy to install and transport
Better performance in high contamination areas
Consistent mechanical and electrical performance throughout the entire service life
Excellent impact resistance
Good resistance to soiling and flashover
Good shock resistance collision resist
Good performance of hydrophobic
Interchangeability- can easily replace existing porcelain insulators
How to choose insulator material?
Each material has its advantages and disadvantages, so the insulator material selection depends on its characters and the requirement of customers.
Porcelain is heavy than other materials and hard to transport and install, but it is cheap and has a long-life performance. Silicone rubber insulator is easy to install, excellent pollution performance, excellent mechanical properties, resistant to weathering, resistant to vandalism, resistance to damage and so on. Glass insulator has better strength.
Chapter 3: Insulator Types
The basic functions of insulators are insulating, supporting and fixing conductor. Each type of insulator also has different functions for different operating conditions.
According to the function: There are more than 5 types, Pin Insulator, Suspension Insulator, Strain Insulator, Spool insulator, Stay Insulator, and so on.
(a)Pin Insulator
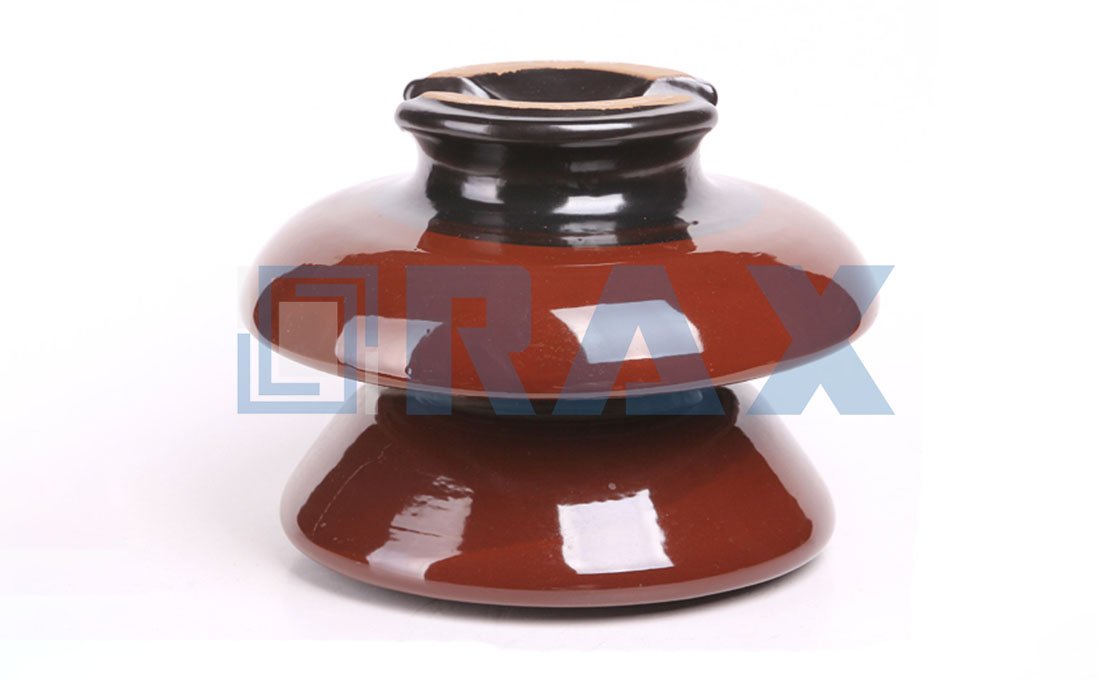

33KV Pin Type Porcelain Insulator
Pin insulators are used at specific points, i.e. at sections for piloting jumpers, etc. Pin insulators are supplied to IEC 62223 or equivalent
Pin type insulators are screwed onto a bolt. The insulators have necks suitable for fastening conductors with tie wire or preformed fittings.
In addition, the following minimum characteristics apply:
| Characteristics | Unit | Value |
| System Voltage | kV | 33 |
| Cantilever Strength | kN | 10 |
| Nominal Diameter | mm | 315 |
| Nominal Height | mm | 240 |
| Minimum Nominal Creepage Distance | mm | 1120 |
| Lightning withstand voltage (1.2/50ms) | kV | 170 |
| Min Power Frequency Flashover Voltage Wet | kV | 70 |
One type of Jingyong Pin Insulator
Each insulator is supplied complete with a hot dip galvanized forged steel pin, complete with nut, lock nut and spring washer complying to BS 3288 Pt 2 large steel.
Line pins shall have a minimum failing load of 10 kN.
Pilot pins shall have a minimum failing load of 0.7 kN.
The ultimate mechanical strength of the pin insulator assembly will be equal to the above cantilever strength.
(b) Line Post Insulator
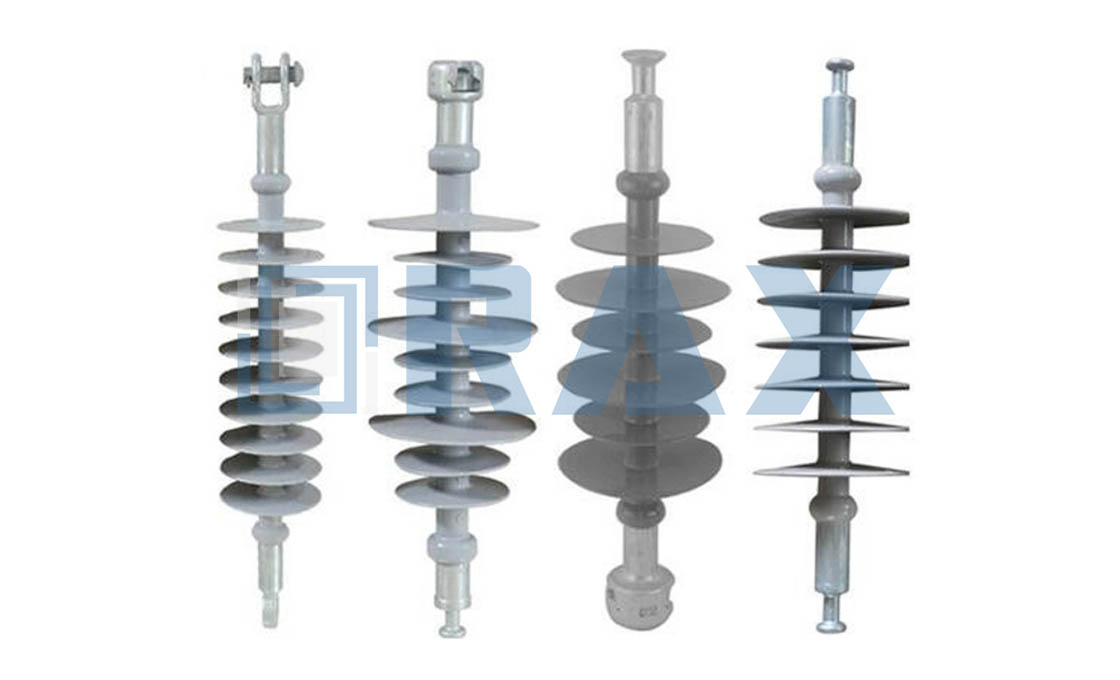
Composite Line Post Insulators
The Line Post insulators give rigid support to a live part which is to be insulated from earth or another live part. These insulators consist of a load-bearing solid core, housing and end fittings attached to the insulating core. It is subjected to cantilever, tensile and compressive loads. This complies with IEC 62223 or an equivalent.
| Characteristics | Unit | Value |
| System Voltage | kV | 33 |
| Cantilever Strength | kN | 20 |
| Nominal | mm | 240 |
| Minimum Nominal Creepage Distance | mm | 1200 |
| Min Power Frequency withstand Voltage Wet (1 min) | kV | 95 |
One type of Rax Industry Line Post Insulator
(c) Strain Insulator (Suspension Insulator)
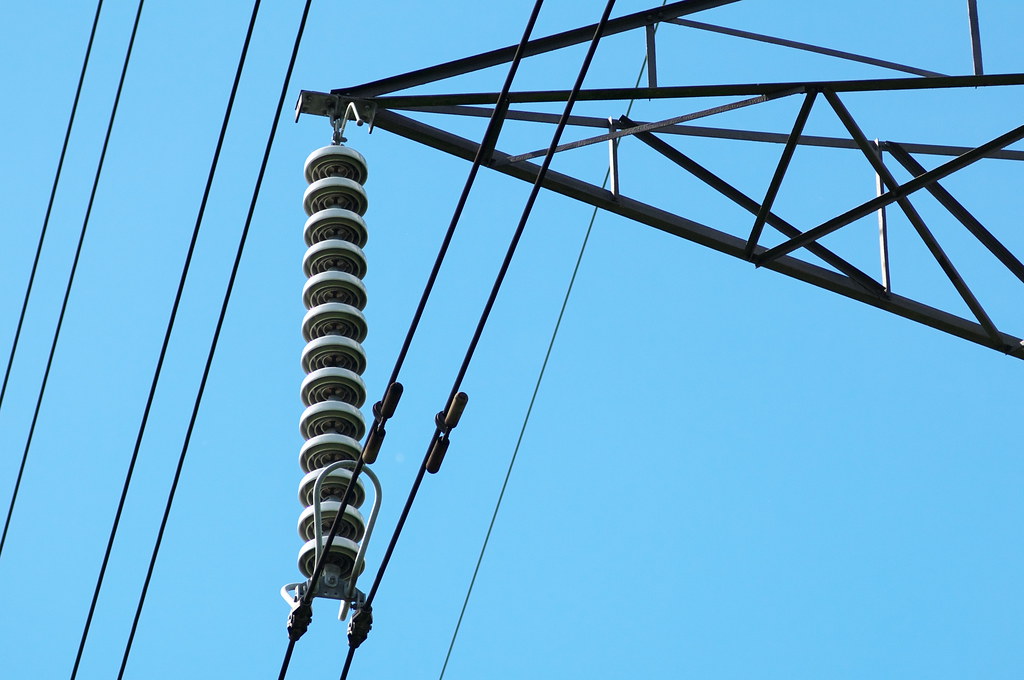

Suspension Insulator
“Suspension Insulator ” and “Strain” insulators are the same thing; when used in the vertical position (with the conductor hanging below) they are called “suspension Insulator “; when used in the horizontal, to dead-end a conductor, they are called “strain Insulator “.
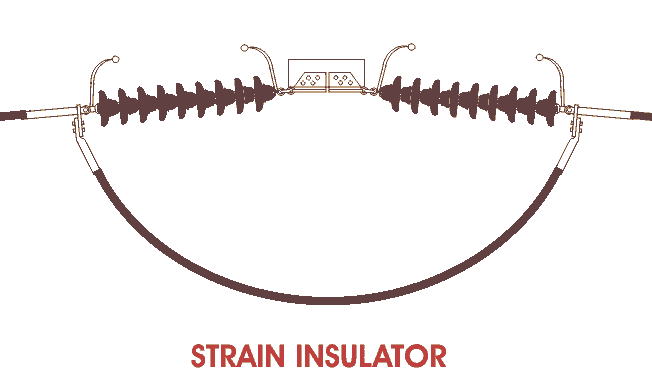
- String Insulators
- String glass insulators are supplied under IEC 62223 (or alternative equivalent)
- Each 33 kV termination assembly consists of three tension disc insulators, ball and socket couplings (16 mm to IEC 120), and a conductor thimble suitable for preformed terminations.
- Each insulator string is supplied with a cross arm fixing comprising terminating straps, and ball hook for cross arm fixing and socket thimble for conductor terminations.
- Composite Polymeric Insulators
The Long rod, Class A, 33kV rated polymeric strain insulators of a composite material, that used on strain structures, complies with IEC 62223. The following table indicates the requirements:
| Characteristics | Unit | Value |
| Nominal system voltage | kV | 33 |
| Dry flashover voltage | kV | 120 |
| Wet flashover voltage | kV | 70 |
| Minimum tensile failing load | kN | 40 |
| Impulse withstand voltage (+) | kV | 200 |
| Impulse withstand voltage (-) | kV | 210 |
| Creepage distance | mm | 1080 |
One type of Rax Industry Strain Insulator
Line tension insulators have a minimum failing load of 40 kN.
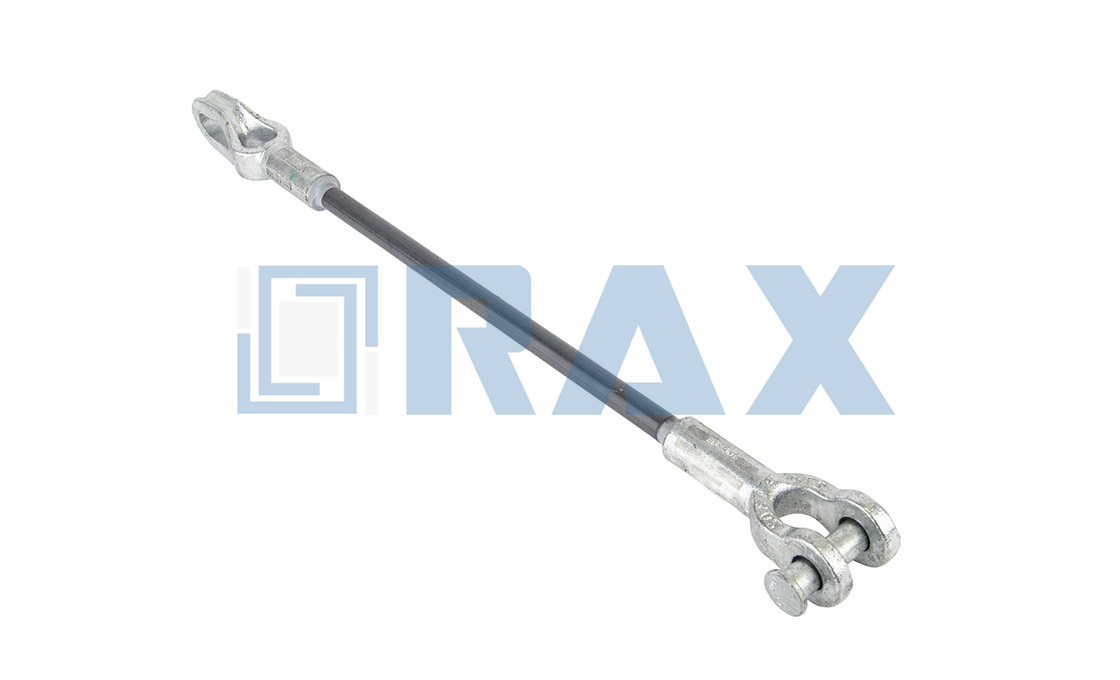
(d) Spool insulator ( Shackle Insulator )
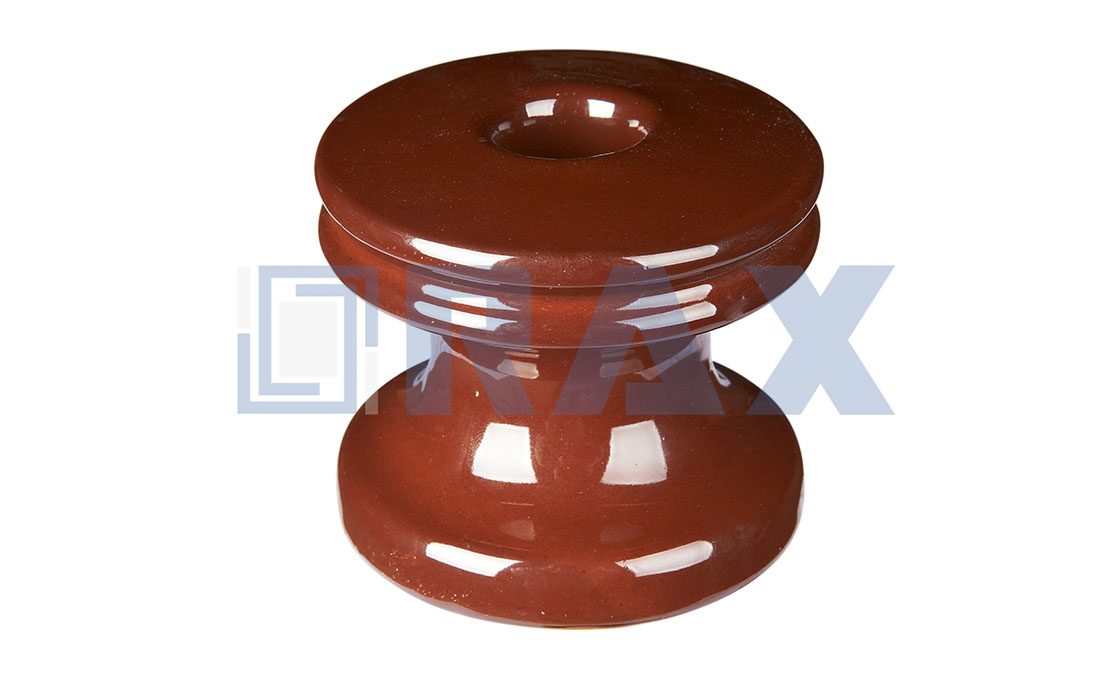

Spool Insulator
Rax Industry spool insulator is also called spool type insulator, shackle insulator. Spool insulator is usually used in low voltage distribution network, both the horizontal or vertical positions.
Rax Industry spool insulator is designed to be assembled with the secondary clevis. Rax Industry spool insulator is made from porcelain.
There are white porcelain insulators and brown porcelain insulators. Rax Industry spool insulators are all small porcelain insulators that are fit for the secondary clevis.
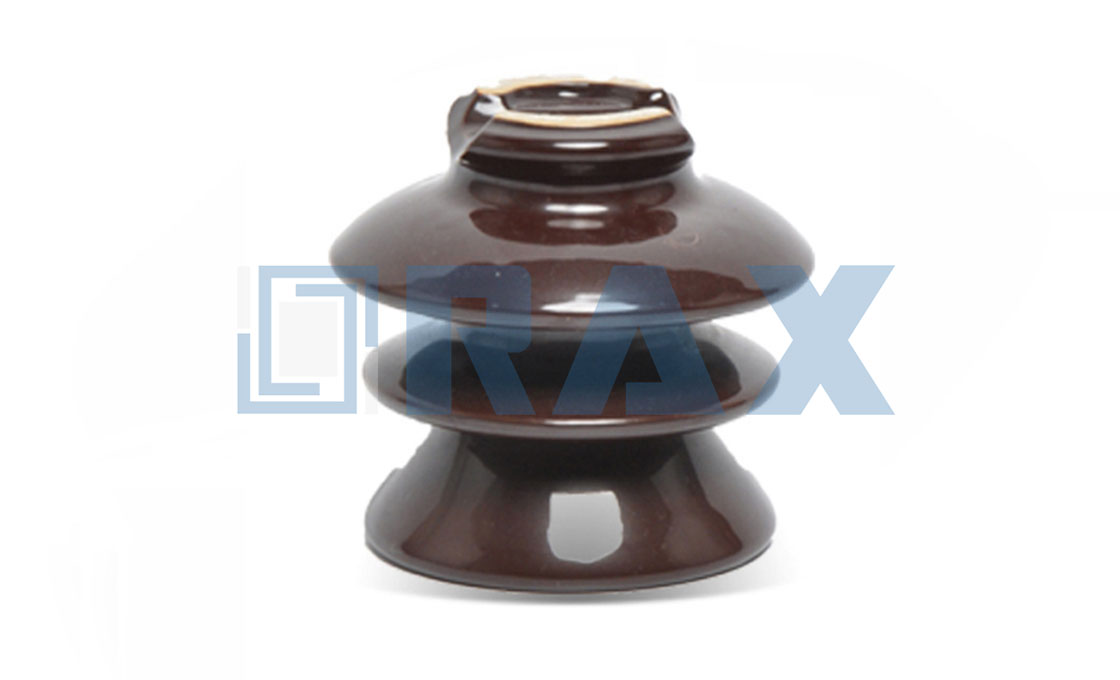
(e) Stay Insulator
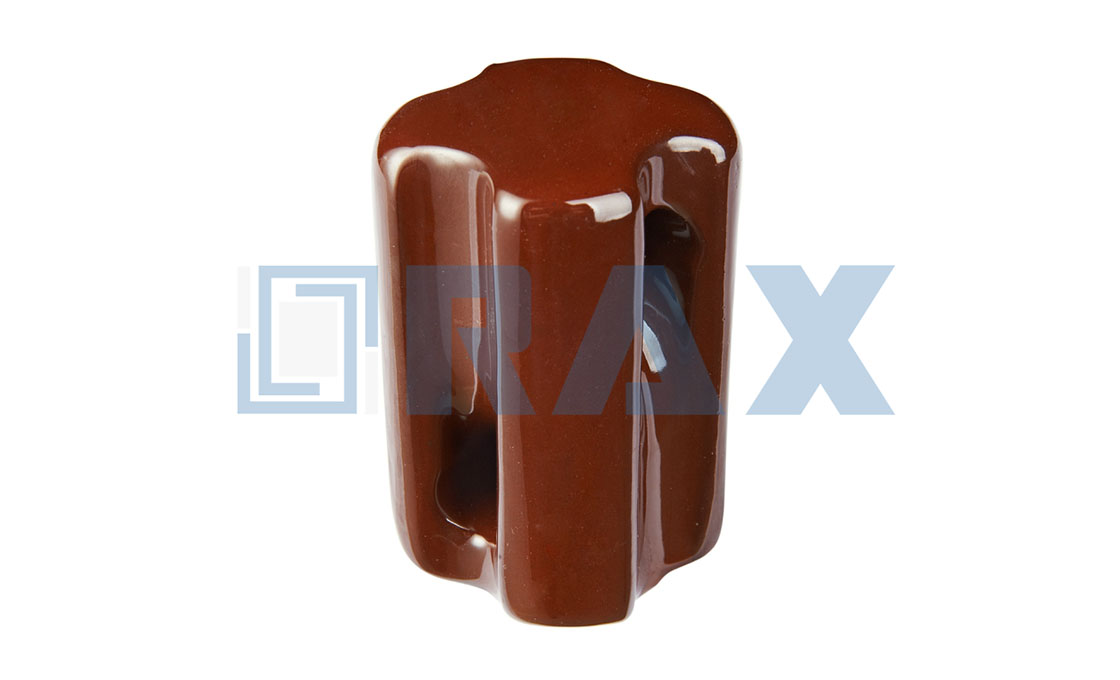

Stay Insulator
Rax Industry stay insulator is also called stay type insulator. The stay insulator is designed to fasten and counterweight the dead end pole by connecting with stay wire or guy grip.
To avoid the dead end pole or terminal pole fall, it should select the suitable types of stay insulators and pole line fittings. Rax Industry stay insulators have the function to avoid the electric conduction on the stay wire by accident.
How do stay insulators function :
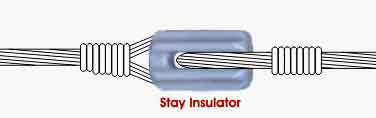
stay insulator
There are two holes in the stay insulator body. The 2 pieces guy grips go through from the hole in the opposite direction. The guy grip will wrap the stay wire to furnish the connection.
For different market there are different ways to connect, We can design the insulator fittings based on the customers’ design and drawings.
According to the voltage, there are 11kv stay insulators and 33kv stay insulators.11kv stay insulator is used on 11kv overhead line network in the power system.
Rax Industry stay insulator is made of glazed porcelain according to BS137 and suitable for operation outdoors.
Chapter 4: Insulator voltage
Insulator voltage ranges from 400v to 1000kv and can be divided into LV, MV, HV, UHV and EHV as per the voltage grade, or distribution, transmission and substation in accordance with their applications in details.
| Low voltage (LV) | 400v, 1kv |
| Medium voltage (MV) | 6kv, 10kv, 11kv, 12kv, 15kv, 20kv, 22kv, 24kv, 25kv, 28kv, 30kv, 33kv, 35kv, 36kv |
| High voltage (HV) | 45kv, 55kv, 66kv, 69kv, 88kv, 110kv, 115kv, 132kv, 220kv |
| Ultra high voltage (UHV) | 300kv, 330kv, 400kv, 500kv, 800kv |
| Extra high voltage (EHV) | 1000kv, above 1000kv |
Common insulator voltage values
| Distribution line insulator voltage | 400v ~ 36kv |
| Transmission line insulator voltage | 66kv ~ 1000kv |
| Substation insulator voltage | 15kv ~1000kv |
Insulator Voltage for Power Lines or Substations
Insulator nominal voltage depends on the system voltage of power lines or substations and should be higher than the system voltage. To meet the different voltage levels, an insulator can be designed into different shapes or length as per the related standards.
Low voltage insulators are a special type of insulator normally used in power distribution lines.
High voltage insulators are a special type normally used in power transmission and distribution lines.
Insulators (voltage higher than 1000v) supplied and installed conform to the standards below:
| IEC 61109 | Composite Insulators for ac overhead lines with nominal voltages greater than 1,000V: Definitions, test methods, and acceptance criteria. |
| BS 3288-2 | Insulator and conductor fittings for overhead power lines; Part 2: Specifications for a range of fittings. |
| IEC: 60060 | High voltage testing techniques – Part 1: General definitions and techniques |
| IEC: 60071-1 | Insulation coordination – Part 1: Terms, definitions, principles and rules. |
| IEC: 60168 | Tests on indoor and outdoor post insulators of ceramic material or glass for systems with nominal voltages greater than 1,000V. |
| IEC: 60433 | Characteristics of string insulator units of the long rod type |
| IEC: 60273 | Characteristics of indoor and outdoor post insulators for systems with nominal voltages greater than 1,000V. |
| IEC: 60720 | Characteristics of line post insulators |
| IEC: 60383 | Test on insulators of ceramic material or glass for overhead lines with a nominal voltage greater than 1,000V |
| IEC: 60383-1 | Insulators for overhead lines with nominal voltages above 1,000V; Part I: Ceramic or glass insulator units for A.C. systems -Definitions, test methods, and acceptance criteria. |
| IEC: 60383-1 | Insulators for overhead lines with nominal voltages above 1,000V; Part 2: Insulator strings and insulator sets for A.C. systems -Definitions, test methods, and acceptance criteria. |
| IEC: 60437 | Methods for Radio Interference (RI) test on high voltage insulators |
| IEC: 60471 | Dimensions of clevis and tongue couplings of string insulator units |
Chapter 5: The important manufacturing Process in Rax Industry
Markings
Each string insulator unit or rigid insulator can be marked with the name or trademark of the customers, the type of insulator and the year of manufacture. In addition, each string insulator unit shall be marked with the specified electro-mechanical or mechanical failing load. These markings will be legible and indelible.
Second-time selection Before Packing
Chapter 6:Inspection and Testing
Testing of Glass Insulator String
Tests are performed in accordance with the relevant IEC standards supplemented by the specific requirements indicated below. These can also be facilitated by Customers.
In the absence of IEC recommendations, the tests will be equivalent at least to the conditions, provisions, and definitions of the above-mentioned standards.
The tests are divided into the following categories:
Routine Tests:
- Visual examination and check for compliance with specifications herein and with the scheduled quantities.
- Mechanical routine tests (string insulators only).
- Electrical routine tests.
Sample Tests:
Tests will be carried out on insulators taken at random from batches offered for inspection. The number of samples will be as indicated in IEC 62223 with a minimum of five units. The samples will be subjected to the following tests after having carried out routine tests in the same order:
- Verification of dimensions
- Temperature cycle test
- Electro-mechanical or mechanical failing load test in accordance with the type of insulator, including thermal-mechanical performance test to IEC 575.
- Puncture test
- Porosity test
- Galvanizing test
In the event of one unit failing to pass any of the sample tests, a further quantity double that of the first quantity will be subject to retesting.
In the event of two or more insulators or metal parts failing to pass any of the sample tests, or if any failure occurs on insulators or metal parts subject to retesting, the complete batch will be considered as not complying with the specification and will be rejected.
Type Tests:
Rax Industry will include in our offers test certificates, including thermal mechanical performance tests carried out in accordance with IEC 575.
The customer representative also can call and witness for type tests to be carried out at the Rax Industry’s Works. Such tests can be on random samples at the discretion of the customer representative.
When such tests are called for they will comprise the following:
- Dry lightning impulse withstands voltage test.
- Wet power frequency withstands voltage test.
An insulating material used in bulk to wrap electrical cables or other equipment is called insulation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
what is an electrical insulator?
An insulator is a vital component used in the electrical systems to prevent unwanted flow of current to the earth from their supporting points.
Insulators are made of insulating materials, porcelain, glass or silicone rubber, they are so insulated that no current can pass through them.
How many types of insulators?
According to the function, more than 5 types:
- Pin Insulator
- Suspension Insulator
- Strain Insulator
- Spool insulator
- Stay Insulator, and so on
According to the voltage:
- 5 grades in common insulator voltage values: Low voltage (LV), Medium voltage (MV), High Voltage (HV), Ultra High Voltage (UHV), Extra High Voltage (EHV).
- 3 grades in insulator voltage for power lines or substations: Distribution line insulator voltage, Transmission line insulator voltage, Substation insulator voltage
What tests should do with insulators?
- Routine Tests: Electrical Routine tests, Mechanical Routine tests, Visual examination and check for compliance.
- Sample Tests, insulators took at random from batches should take Verification of dimensions, Temperature cycle test, mechanical failing load test and so on.
- Type Tests, thermal mechanical performance tests carried out under IEC 575: Dry lightning impulse and Wet power frequency withstand voltage test.
All the tests are performed in accordance with the relevant IEC standards supplemented by the specific requirements.
How to choose the reliable insulator manufacturers?
The manufacturer and supplier should have adequate resources and capacity to supply the best insulators for overhead lines.
Checking what other people are saying about the insulators from a particular manufacturer. This is possible by reading the insulator reviews.








