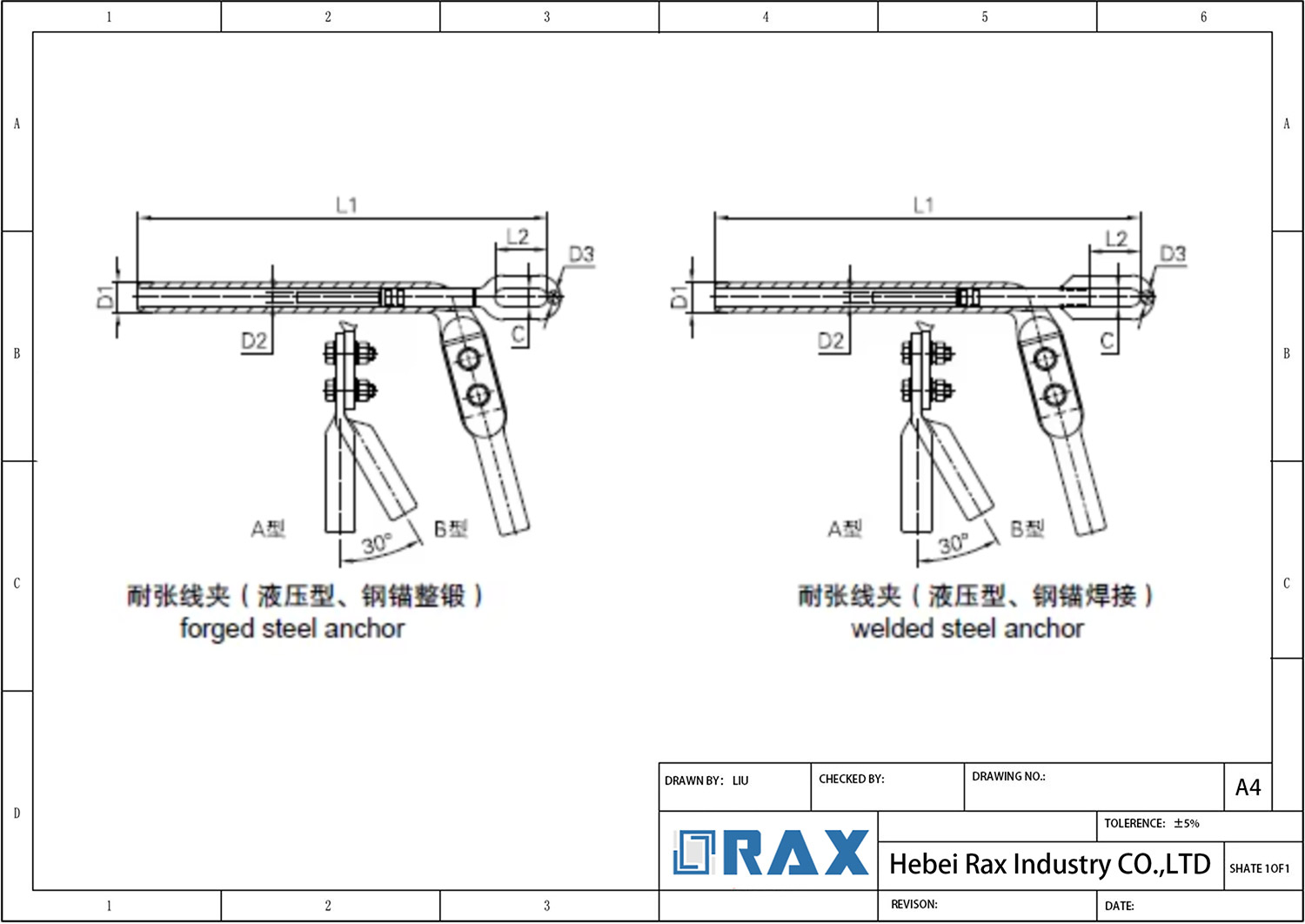
Compression Dead-end
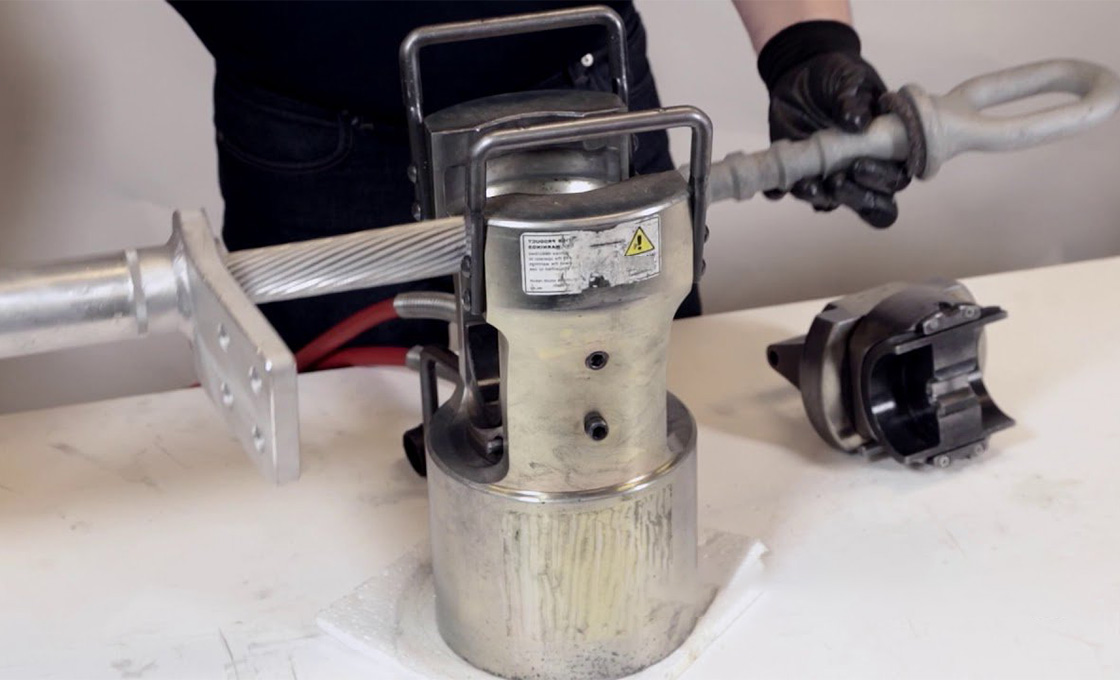
Compression Dead-ends are electrical connectors in overhead transmission systems, specifically designed for ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced) and AAC (All Aluminum Conductors). Also referred to as compression dead-end assemblies, these products serve the critical function of securing conductors at termination points. They consist of an aluminum body that compresses around the outer diameter of the conductor and a steel eye that grips the steel core. The compression process ensures that these assemblies achieve a holding strength of 95% or more of the conductor’s rated breaking strength, adhering to ANSI C119.4 standards. Compression Dead-ends can be used with industry-standard presses and dies for installation, making them versatile in various applications.
To use Compression Dead-ends effectively, they should be paired with compatible conductors such as ACSR or AAC types. The assembly includes components like a felt washer and filler plug, enhancing its reliability and performance. The design allows for continuous operation at temperatures up to 125°C, with a two-hour emergency rating of 150°C. Notably, the dead end pad features a 15° angle, facilitating terminal connections in both 0° and 30° configurations. This adaptability makes Compression Dead-ends suitable for various installation scenarios in power transmission lines.
Key Features:
- Achieves a minimum of 95% of conductor rated breaking strength
- Supports continuous operation at high temperatures
- Compatible with standard compression tools for easy installation
- Designed for full tension use in overhead transmission systems
-
Includes essential components for enhanced reliability
Compression Dead-end Drawing
| Cat.No. | Applicable Con ductor | Dime nsion s(mm) | Grip strength(kN) | |||||
| D1 | D2 | D3 | C | L1 | L2 | |||
| NY-95/15A(B) | JL/G1A-95/15 | 26 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 390 | 55 | 33.5 |
| NY-95/20A(B) | JL/G1A-95/20 | 26 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 390 | 55 | 35.4 |
| NY-120/20A(B) | JL/G1A-120/20 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 408 | 55 | 39 |
| NY-120/25A(B) | JL/G1A-120/25 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 430 | 55 | 45.5 |
| NY-150/20A(B) | JL/G1A-150/20 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 438 | 65 | 44.3 |
| NY-150/25A(B) | JL/G1A-150/25 | 30 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 447 | 65 | 51.5 |
| NY-150/35A(B) | JL/G1A-150/35 | 30 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 465 | 65 | 62 |
| NY-185/25A(B) | JL/G1A-185/25 | 32 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 445 | 65 | 56.5 |
| NY-185/30A(B) | JL/G1A-185/30 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 473 | 65 | 61.5 |
| NY-185/45A(B) | JL/G1A-185/45 | 32 | 18 | 18 | 22 | 490 | 65 | 76.5 |
| NY-240/30A(B) | JL/G1A-240/30 | 36 | 16 | 18 | 22 | 510 | 65 | 72 |
| NY-240/40A(B) | JL/G1A-240/40 | 36 | 16 | 18 | 22 | 510 | 65 | 79.2 |
| NY-240/55A(B) | JL/G1A-240/55 | 36 | 20 | 20 | 24 | 565 | 65 | 97 |
| NY-300/15A(B) | JL/G1A-300/15 | 40 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 510 | 65 | 65 |
| NY-300/20A(B) | JL/G1A-300/20 | 40 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 523 | 70 | 72 |
| NY-300/25A(B) | JL/G1A-300/25 | 40 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 527 | 70 | 79.3 |
| NY-300/40A(B) | JL/G1A-300/40 | 40 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 547 | 70 | 88 |
| NY-300/50A(B) | JL/G1A-300/50 | 40 | 16 | 18 | 26 | 557 | 70 | 98.3 |
| NY-300/70A(B) | JL/G1A-300/70 | 42 | 18 | 20 | 26 | 610 | 78 | 122 |
| NY-400/20A(B) | JL/G1A-400/20 | 45 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 560 | 70 | 84.5 |
| NY-400/25A(B) | JL/G1A-400/25 | 45 | 14 | 18 | 24 | 560 | 70 | 91 |
| NY-400/35A(B) | JL/G1A-400/35 | 45 | 16 | 20 | 26 | 580 | 78 | 99 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
 What is a Compression Dead-end?
What is a Compression Dead-end?
A compression dead-end is a type of electrical connector used to terminate conductors, ensuring a secure and reliable connection. It consists of an aluminum body and a steel eye, designed to handle high tension and maintain electrical continuity. These connectors are essential for overhead power lines and are used with various conductor types.
How do I install a Compression Dead-end?
To install a compression dead-end, first prepare the conductor by cleaning it and ensuring it’s straight. Insert the conductor into the dead-end body, mark it for cutting, and then use a compression tool to crimp the aluminum body onto the conductor. Follow specific instructions for die sizes and overlap compressions for optimal results.
What are the standard sizes of Compression Dead-ends?
Compression dead-ends come in various standard sizes to accommodate different conductor diameters. Common sizes include 1/0, 2/0, and 3/0 AWG for ACSR conductors. As a leading manufacturer, we can customize sizes according to customer requirements.
What materials are used in Compression Dead-ends?
Compression dead-ends typically consist of an aluminum body and a steel eye. The aluminum provides excellent conductivity while the steel eye ensures strength and durability under high tension conditions.
Can Compression Dead-ends be reused?
No, compression dead-ends should not be reused once installed. Reusing them can lead to improper connections and potential current leakage, compromising the safety and functionality of the electrical system.
Where are Compression Dead-ends commonly used?
Compression dead-ends are widely used in overhead power lines, including low, medium, and high voltage applications. They provide reliable connections for ACSR, AAC, and AAAC conductors in various transmission and distribution systems.
What is the holding strength of Compression Dead-ends?
Compression dead-ends are designed to achieve a holding strength of at least 95% of the rated breaking strength (RBS) of the conductor they are used with. This ensures they can withstand significant mechanical forces without failure.












 What is a Compression Dead-end?
What is a Compression Dead-end?